
LOS 31 (a) Explain expected exposure, the loss given default, the probability of default, and the credit valuation adjustment. The aim of this paper is to present an approach to estimate the probability of default of non-financial corporations using data from the CRC, complemented with. The third and at the same time the broadest approach, known as Advanced IRB, enables banks to estimate all risk parameters. The recovery rate is the proportion that can be recovered in a default event. The present value of the expected loss.Įxpected exposure (EE) is the amount that an investor or bondholder stands to lose at any given point in time in case of default.At month 10 into the loan, there is a probability of survival of 80. The probability of default is a metric that lenders use to assess risk on customers, group them into similar risk bands, and determine what interest rate to. LGD is calculated as the inverse (1 minus) the anticipated recovery rate on loans secured by specific underlying assets.
CALCULATE PROBABILITY OF DEFAULT HOW TO
There are four credit risk measures for fixed income securities. Can someone help with how to calculate the annualized probability of a loan default given: 70 probability of survival (30 default) over the next 20 months Edit: I should have been more specific in my question. Key Takeaways LGD represents a lender’s anticipated credit loss should a borrower trigger an event of default that requires the creditor to liquidate the borrower’s collateral assets. A probability of default (PD) is already assigned to a specific risk measure, per guidance, and represents the percentage expectation to default, measured most frequently by assessing past dues. Credit spread rewards exposure to credit risk. Probability of Default/Loss Given Default analysis is a method used by generally larger institutions to calculate expected loss. On the other hand, credit spreadis the difference between the yield to maturity of credit risky, zero-coupon bond, and a risk-free zero-coupon bond.
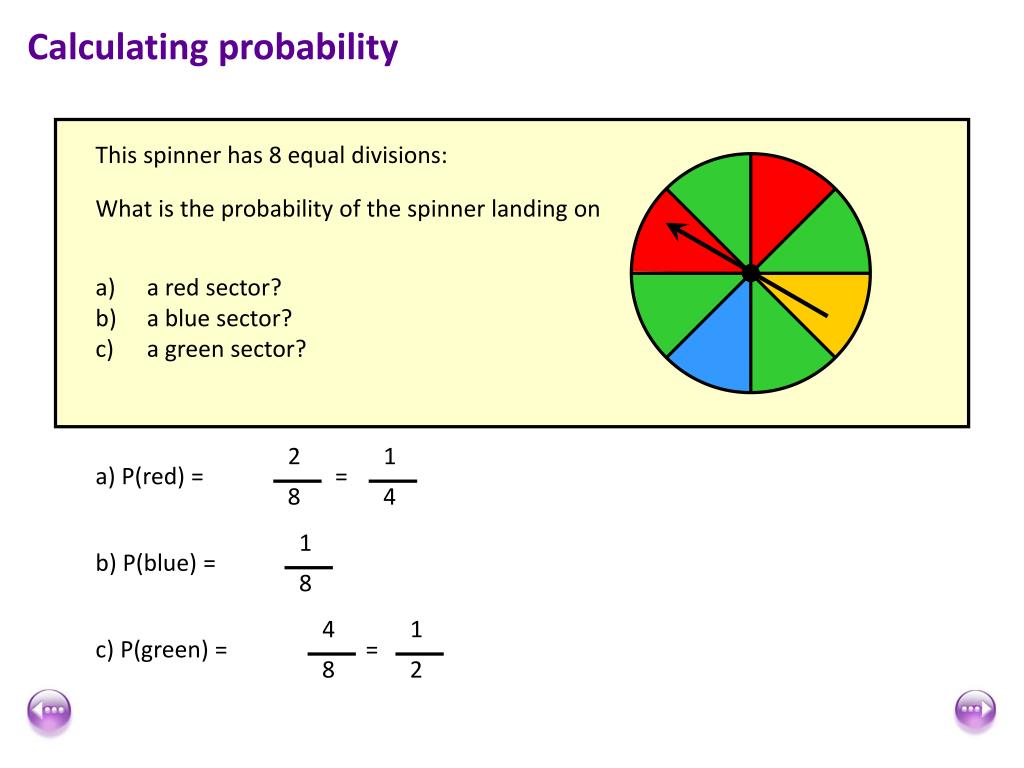
Credit risk is the risk of default or delay in making interest or principal payments on a loan. Step 1: Define the default Before we actually get to probability of default, lets take a look at what it is.

The probability of default can be calculated as follows: (19. Ryan OConnell, CFA, FRM explains how to calculate Probability of Default (PD), Loss Given Default (LGD), and Expected Loss (EL) in Microsoft Excel. The PD is calculated by analyzing various factors such as the borrowers credit history, financial health, and current economic conditions. having read solutions to the exam questions, I would recommend just to do something (assume normality, for example), if you get stuck 🙂. The risk-neutral probability of default is the probability that the put finishes in-the-money. The default probability of corporation is calculated according to the credit spread and the loss given default of corporate bond. I did some simulations in Excel, and found that in 500 tries I had no default, I suspect there is a problem in examiner’s solution with calculation of annual deviation. In Q3 from December 2008, for example, examiner in answers assumes that cashflow is distributed normally, then he calculates expected annual cashflow and its volatility, and finally probability that cash outflow is greater than cash in hand. Volatility of Rs (which is actually normally distributed) is used in Black – Scholes formula.Īssume that V – value of assets of the comany today, F – debt payable (in t years), if V distributed lognormally, using black-scholes formula you can calculate ‘value firms equity as european call option’ (from BPP study text):ĭ1=(ln(V/F)+(r+0,5*sigma^2)t/(sigma*sqrt(t))ĭ2=d1-sigma*sqrt(t), where sigma is volatility of ln(V) (in BPP study text sigma is volatility of V, which is inconsistent with Black-Scholes model assumptions)ġ-N(d2) is the probability of default (when option is out of the money). We have internal ratings (again based on financials) that we are using for. Calculate PDs for each client based on their financial Statements, 2. Could you, please, advise me how to do that I think we have two Options: 1.
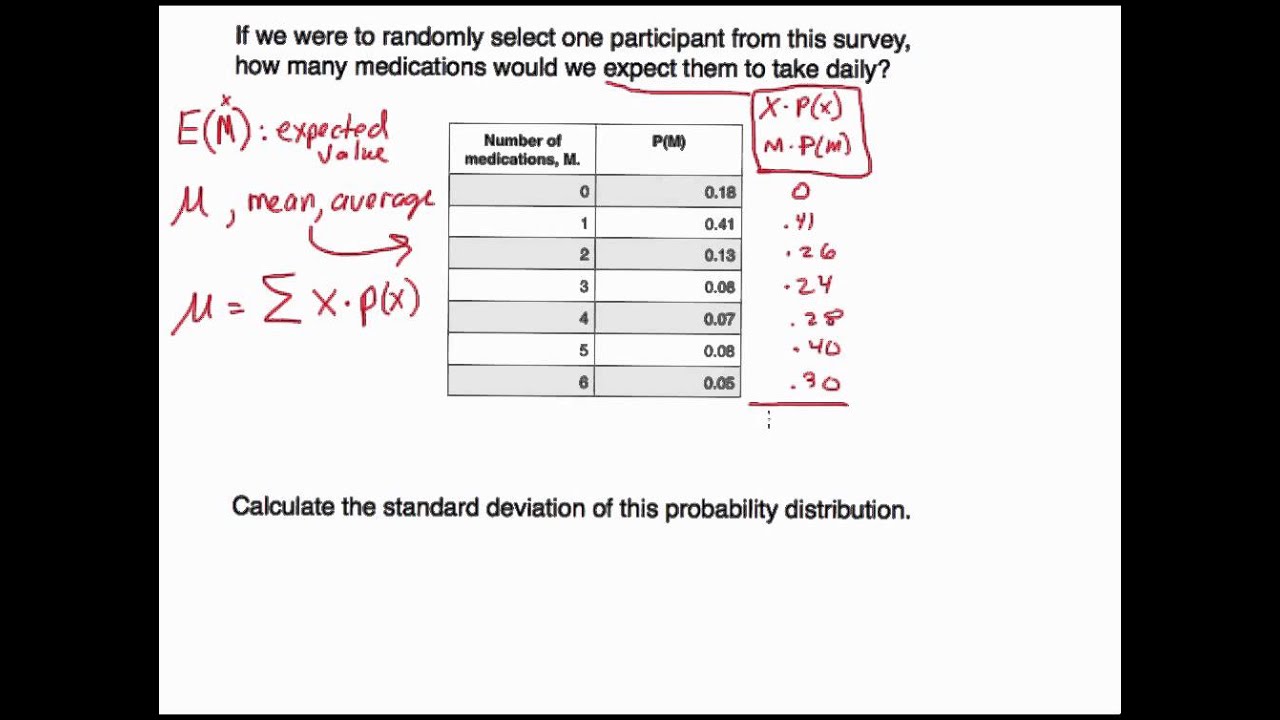
You are given (1 x)20 0.7 ( 1 x) 20 0. I have to calculate probability of default (PD) rates for our clients (I am working in a Bank) based on clients financials.
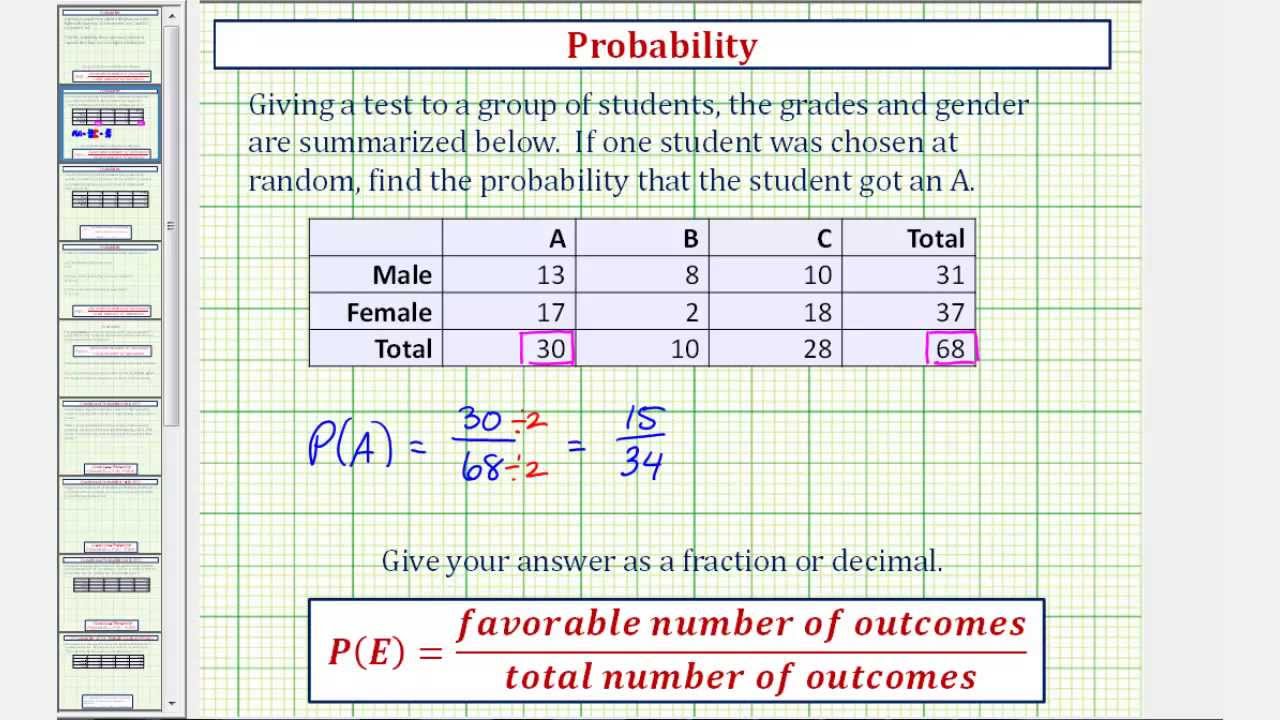
Then S/S0=exp(Rs), assuming continious compounding. Assuming a constant rate x x of default over each month, the rate of survival after n n months is (1 x)n ( 1 x) n. S0 – current price, S – price in one year (lognormally distributed random variable). Black – Scholes model assumes that underlying stock is distributed lognormally.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
